INTRODUCTION

Clinical imaging is likely to play a pivotal role in diagnosis as well as treatment of accidents. The advent of artificial intelligence, or PC-based knowledge, has brought a revolutionary change in the field of clinical imaging. Artificial intelligence evaluations are being used to look at clinical images, such as X-rays, CT scans, X-rays, and ultrasounds, with almost perfect accuracy and credibility. This has critical implications for patient cognition, being previous region of disturbances, but more accurate estimations-and again attempted treatment plans.
Clinical Imaging Systems
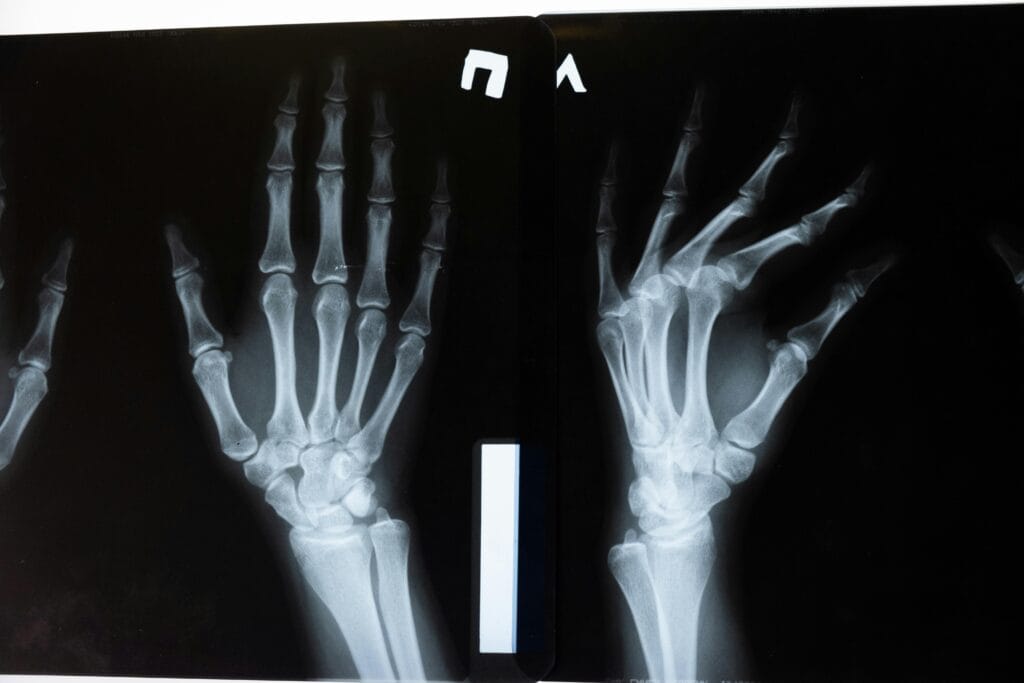
Clinical imaging systems use a variety of technologies to produce images of the body for conscious purposes. Such images can help doctors see inner organs, tissues, and structures that further assist them in the diagnosis and treatment of many problems and conditions. Conventional clinical imaging modalities are:
X-sends: Employ the use of electromagnetic radiation to take radiographies of bones and other dense tissues.
Computation tomography (CT):: Utilizes X-rays of assistance in taking photographs of cross-sectional section of the body.
Scanning resonating imaging (X-ray): Utilizes interacting fields along with radio waves in making artificial pictures of delicate tissues.
Ultrasound: Utilizes sound waves in making pictures of inner organs and tissues.
The Management of PC Information in Clinical Imaging
PC based information computations, specifically replicated data and titanic learning, can be used for clinical imaging to regain reasonable accuracy and limit. These strategies can segregate large datasets, artificial intelligence that could potentially scan for huge volumes of clinical images and find models that may be normal for degradation losses, or anomalies which could be invisible to human vision. Moreover, the quality of images can be improved by artificial insightful limit that can control the likelihood of the clinical image, reducing the noise as well as lags.
Help end: man-made information can assist radiologists with diagnosing issues by giving second emotions and including suspected characteristics .
Focus on trouble movement: man-created hypothesis can appraise the improvement of issues by reviewing changes in clinical pictures over time.
Re-try treatment plans: replications of information can help improve treatment plans by researching patient-express information and identifying best treatment options .
Unambiguous Motives behind PC based information in Clinical Imaging
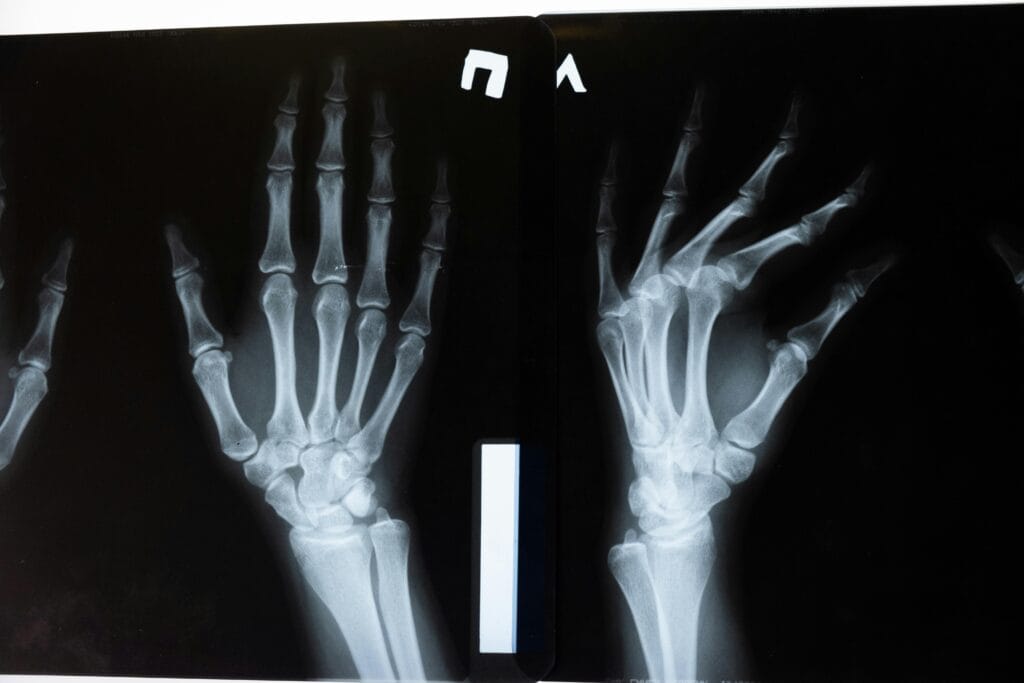
Hazards improvement seeing assertion: Computer-based information can be used to see the beginning stage disorders, such as chest pain, cell breakage in the lungs, and prostate pollution, by scrutinizing medical images for anomalies.
Brain development certification: Computer-based information can help in seeing hazardous new developments in the brain and assess their size and area.
Cardiovascular torture affirmation: artificial information can see anomalies in the heart and arteries, like aneurysms and atherosclerosis.
Bone break clearness: artificially made data can unmistakably perceive bone breaks, even in complex cases.
Combine movement monitoring: Computer-based data can monitor the progression of diseases, such as degenerative sclerosis and Alzheimer’s condition, by dissecting changes in medical pictures over a considerable length of time.
Radiomics: man-made care can eliminate quantitative parts from medical images, called radiomic features, which can provide key information on the characteristics of stages of disease and many types of degradations.
Redirecting images: man-made intelligence capacity can perform the chance of clinical pictures by copying them from deficient or loud information.
Clinical picture selection: man-made information can include clinical pictures from different modalities or time focuses to help connection and assessment.
Benefits of man-made information in Clinical Imaging
Set working on illustrative precision:
man-made information can presumably and continually outwork on the exactness of clinical choice, actuating prior unveiling of contaminations and actually convincing treatment.
Even further made limit: PC based information can smoothen the process in medical imaging, thus reducing the required timeframe to assess a picture and understand it.
Lowered costs: PC based information can allow for reducing clinical thinking costs by enhancing true precision, and further lowering the prime for intangible tests and frameworks.
Better established outcomes: man-made information can facilitate progressive tolerant results by enabling prior area and treatment of infections .
Easier consent to mind: man-made information can also facilitate consent to clinical imaging affiliations, especially in remote or underserved locale.
Improvement in clinical appraisal: PC based data can expedite clinical evaluation by associate new openings and pieces of information from clinical picture appraisal.
Weights and Tests
Whereas recreated insight provides exemplary advantages to clinical imaging, there are also indications and considerations to debate with:
Data quality: The possibility of clinical pictures is basic to cautious man-made care based examination. Guaranteeing unimaginable pictures is basic.
Bias: PC based data analysis can be biased if constructed on data not representative of everyone. Address affinity should ensure equitable and unbiased findings.
Ethics: The use of PC based data in clinical imaging raises ethical issues in data security, patient door, and potential of affinity in the calculations involved in PC based data analysis.
Coexistence with other plans: justification of computer-based information: making clinical imaging devices come to life, integration with clinical benefits designs can be very complicated and tiresome.
Compliance with the law:

AI-based clinical imaging applications should meet the core guidelines and standards which might include HIPAA in the US and GDPR in the European Union. Future Perspective
The evident predetermination of man-made information in clinical imaging is astonishing, with the ability to change how clinical thought is displayed. As man-made information movement proceeds and the responsiveness of clinical imaging data expands, we can expect on an incredibly essential level further imaginative applications that will advantage patients and clinical advantages suppliers.
Conclusion
Man-made information is a magnificent asset that would revive, as much as possible, and credibility of clinical imaging. Clinical thought providers can improve understanding results, minimize expenses, and enhance the discipline of clinical imaging with replicated data examinations. As man-acquired information ground keeps on making, we should expect to see more usefully innovative applications that will change how we assessment and treat ailments.

